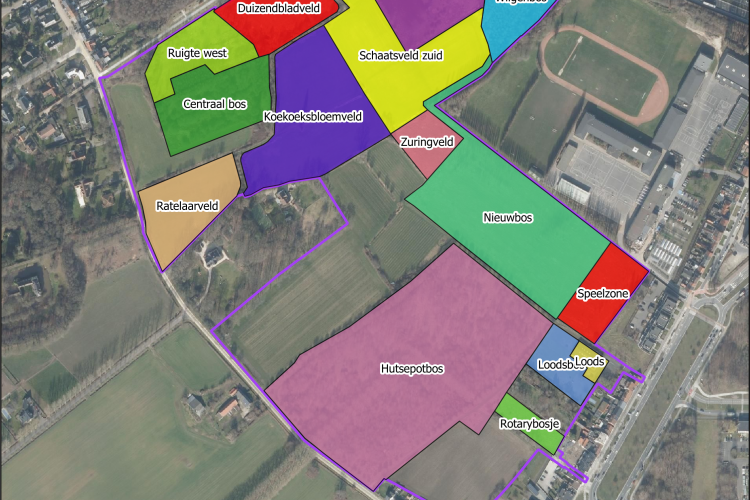
PSB Forest
We are also working on a project – together with Natuurpunt - that involves forest restoration and biodiversity. Updates soon!
Find out what species are found in this forest on waarnemingen.be!
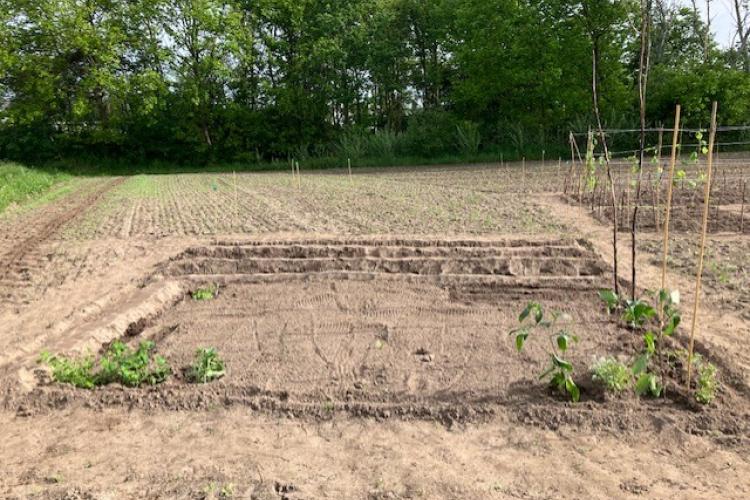
PSB Garden
A currently unused field plot close to PSB at the Tech Lane Ghent Science Park will be used for non-GMO field trials. The idea is to give students, postdocs, and personnel of VIB the opportunity to experiment with different plants and crops and to build a community garden this way. The land is currently being prepared for planting and photos will be posted regularly to show the progress, so stay tuned.
DE MICROCAST: DE PODCAST OVER EEN MICROSCOPISCHE WERELD MET EEN MACROSCOPISCHE IMPACT
In Dutch - In deze tweewekelijkse podcast daalt een groep jonge wetenschappers af naar de wonderbaarlijke wereld van micro-organismen. Wat hebben deze kleine wezens voor ons betekend in het verleden, waarvoor worden ze in ons dagelijks leven gebruikt en wat kunnen we met microben allemaal doen in de toekomst? Je zal versteld staan van het verraad, de intriges en de haat-liefde verhoudingen die zich afspelen in deze microscopische wereld!