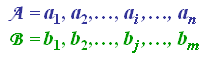|
|
|
|
|
|
||
| Home | ||
| Tutorial | ||
| Case Study | ||
| Manual | ||
|
|
DTW algorithm | |
| Thanks | ||
| Download | ||
| DTW algorithm | ||
|
Dynamic time warping (DTW) is a time
series alignment algorithm developed originally for
speech recognition(1). It aims at aligning two
sequences of feature vectors by warping the time
axis iteratively until an optimal match (according to a suitable metrics) between the two sequences is found.
Consider two sequences of feature vectors:
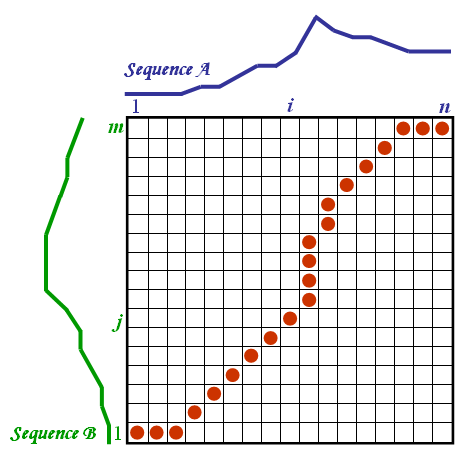
The two sequences can be arranged on the sides of a grid, with one on the top and the other up the left hand side. Both sequences start on the bottom left of the grid.
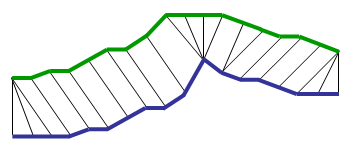
Inside each cell a distance measure can be placed, comparing the corresponding elements of the two sequences. To find the best match or alignment between these two sequences one need to find a path through the grid which minimizes the total distance between them. The procedure for computing this overall distance involves finding all possible routes through the grid and for each one compute the overall distance. The overall distance is the minimum of the sum of the distances between the individual elements on the path divided by the sum of the weighting function. The weighting function is used to normalise for the path length. It is apparent that for any considerably long sequences the number of possible paths through the grid will be very large. The major optimisations or constraints of the DTW algorithm arise from the observations on the nature of acceptable paths through the grid:
The foregoing constraints allow to restrict the moves that can be made from any point in the path and so limit the number of paths that need to be considered. The power of the DTW algorithm is in the fact that instead finding all possible routes through the grid which satisfy the above conditions, the DTW algorithm works by keeping track of the cost of the best path to each point in the grid. During the calculation process of the DTW grid it is not known which path is minimum overall distance path, but this can be traced back when the end point is reached. A detailed technical presentation of the DTW algorithm can be downloaded from here DTW algorithm.
(1) Sakoe,H. and Chiba, S. Dynamic programming algorithm optimization for spoken word recognition. IEEE Trans. on Acoust., Speech, and Signal Process., ASSP 26, 43-49 (1978).
|